

| Length: | 14 ft (4.3 m) |
|---|---|
| Diameter: | 15 in (377 mm) |
| Tailspan: | 6.5 ft (2 m) |
| Weight: | 2000 lbs (900 kg) |
| Filling: | 530 lbs (240 Kg) of Tritonal |
| Guidance: | Infrared laser |
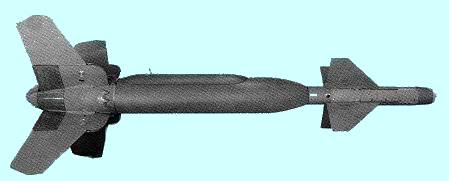 The GBU-24/B was originally designed to be
installed on the MK-84 General Purpose Bomb. In 1985 with the availability of the BLU-109/B Penetrator bomb the Paveway III was made to adapt it and
thus was redesignated GBU-24A/B. The LLLGB is currently carried on the CF-18 Hornet
aircraft.
The GBU-24/B was originally designed to be
installed on the MK-84 General Purpose Bomb. In 1985 with the availability of the BLU-109/B Penetrator bomb the Paveway III was made to adapt it and
thus was redesignated GBU-24A/B. The LLLGB is currently carried on the CF-18 Hornet
aircraft.
GBU stands for Guided Bomb Unit in some books and as Glide Bomb Unit in others.
The difference between the Paveway II and the Paveway III is that the Paveway III can be released at a lower altitude as it will do a "bump-up" maneuvers by climbing 500 feet (because of its large tail assembly which provides it with enough lift to do so) or so to be able to detect the target then dive on it.
 Since we're on the topic of detecting the
target, lets see how it is done. The target has to be designated (painted or illuminated)
with a laser beam. This laser beam can originate from a ground or an aircraft mounted
designator. When the laser beam from a designator hits the target it is reflected in all
directions. The Paveway while trying to maintain a level flight will detect this
reflection and direct itself towards it. Since the laser is in the infrared spectrum, it
can be used day or night and is not visible to the naked eye.
Since we're on the topic of detecting the
target, lets see how it is done. The target has to be designated (painted or illuminated)
with a laser beam. This laser beam can originate from a ground or an aircraft mounted
designator. When the laser beam from a designator hits the target it is reflected in all
directions. The Paveway while trying to maintain a level flight will detect this
reflection and direct itself towards it. Since the laser is in the infrared spectrum, it
can be used day or night and is not visible to the naked eye.
If you have any questions on the GBU-24A/B Low Level Laser Guided Bomb, send me an email and I'll see what I can do......
Copyrightę 1997 F. Martel. All rights reserved
http://gunplumbers.org/gbu24a.html
Last updated: 18 November 2007
Comments or suggestions: Webmaster